Using chatbots in the medical field - GenAI and the source verification problem
Source:
arXiv.org
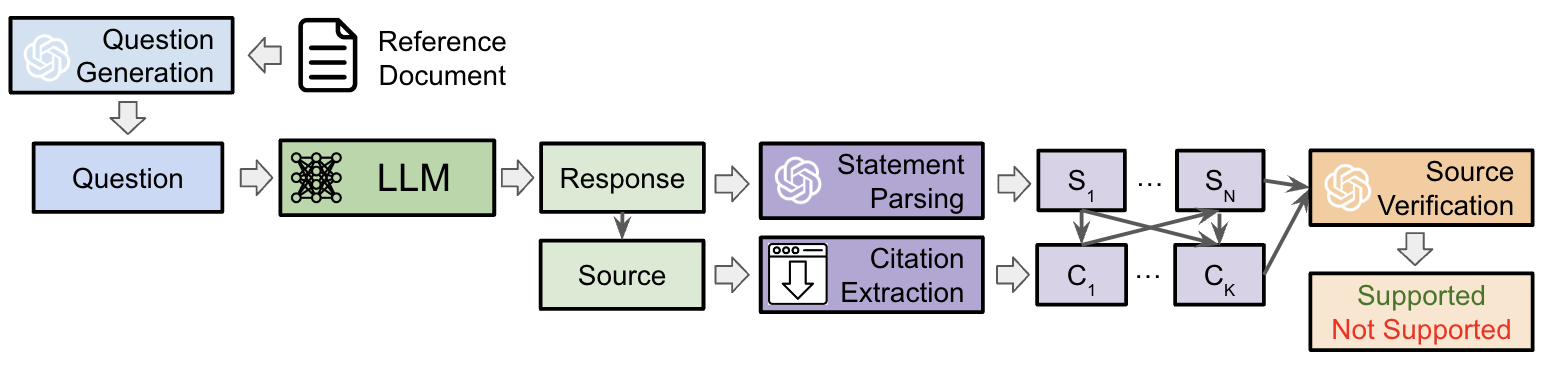
Fig.1: Diagram of the SourceCheckup evaluation pipeline.
Healthcare professionals are increasingly using chatbots to answer questions they or their patients may have. If the answers provided by generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools (GenAI) are factual and the sources cited. However, there is a risk that large language models (LLMs) may generate answers that are incorrect or lacking in veracity. This phenomenon is commonly referred to as “hallucination”.
This is the problem that researchers Kevin Wu, Eric Wu, Ally Cassasola, Angela Zhang, Kevin Wei, Teresa Nguyen, Sith Riantawan, Patricia Shi Riantawan, Daniel E. Ho, James Zou set out to address.
In this study, researchers Kevin Wu et al. set out to verify whether commercial LLMs such as ChatGPT-4 (OpenAI), Gemini Pro (Google-Alphabet), Claude v2.1 (Anthropic) or Mistral Medium (Mistral.ai) correctly indicate their results and sources.
An important point to note is that the researchers are using 2 versions of ChatGPT, one called Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), which enables generative AI tools to access the Internet network in real time. Another version, known as the Application Programming Interface (API), does not offer live access to the Internet.
After recalling the operating principles of generative AI tools, researchers Kevin Wu et al. define the automated evaluation framework.
To begin, Kevin Wu et al. define an automated evaluation framework for LLMs. Named “SourceCheckup”, this automated evaluation framework consists of a set of 4 automated tasks under ChatGPT-4. This set includes:
- Question generation ;
- LLM question answering ;
- Instruction source analysis;
- Source verification.
Below are the details of the test protocol for the creation of “ SourceCheckup ”:
Module 1 - Question generation
Using ChatGPT-4 and a strict generation protocol. Document sources were framed from 3 sites:
MayoClinic, a site providing patient information ;
UpToDate, a site providing articles aimed at doctors with an in-depth level of medical detail;
Reddit r/AskDocs, a site offering spontaneous questions that often have no clearly defined answers.
Module 2 - Answering LLM questions:
Each LLM questioned must provide a short answer and an exhaustive list of their sources. A second attempt is granted when an LLM does not provide a source in its answer.
Module 3 - Analysis of instruction sources:
Decomposition of each response and analysis of each response URL in order to verify each statement. Following a very strict protocol (using ChatGPT-4), the researchers segmented each response so that they could be verified individually.
Module 4 - Source verification:
The source validation protocol comprises 3 indicators:
Indicator 1: Source URL Validity, result based on the response to an HTTP request (code 200).
Indicator 2: Statement-level support, based on the relevance of a response. For each response from a GenAI tool, the tool must provide at least 1 source of information.
Indicator 3: Response-level support, indicates the percentage of responses in which each statement is justified.
The results of Kevin Wu et al.'s research team have first of all made it possible to develop a technique for validating the results generated by LLMs using “ SourceCheckup ”.
But also, the results of the Kevin Wu et al. research team highlight the problem of hallucinations (extrapolation of results) of generative AI tools. This problem is linked to their training methods.
The final point highlighted by this scientific study is that, in the medical field, there is dissension between certain medical experts.
To begin with, GPT-4 generates a question based on a given medical reference text. Each LLM evaluated produces a response based on this question, which includes the text of the response as well as any URL sources. The LLM response is analysed for individual medical statements, while the URL sources are downloaded. Finally, the source verification model is asked to determine whether a given medical statement is supported by the source text and to give reasons for its decision.
Bibliography: (text APA)
Wu, K., Wu, E., Cassasola, A., Zhang, A., Wei, K., Nguyen, T., & Zou, J. (2024). How well do LLMs cite relevant medical references? An evaluation framework and analyses. arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.02008.

